In the vast tapestry of communication history, few threads are as intricately woven and enduring as Morse code.
Originating in the early 1830s, this ingenious system of dots and dashes revolutionized long-distance communication, serving as the heartbeat of telegraphy and playing a pivotal role in critical moments throughout history.
As we embark on this guide, we aim to unravel the enigma of Morse code, shedding light on its historical significance and exploring the contemporary realm of Morse Code Translators.
Morse code, conceived by Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail, is a testament to simplicity’s power in conveying complex messages. Beyond its telegraphic origins, Morse code continues to captivate enthusiasts, technophiles, and curious minds alike.
This Morse Code Translator guide serves as a beacon, lighting the historical narrative, showcasing the diverse applications of Morse code in the modern era, and providing a compass to navigate the world of Morse Code Translators.
Whether you’re a novice intrigued by the elegance of dots and dashes or a seasoned Morse code fan, join us on this journey as we decode the language that has resonated across time and explore the tools that bring Morse code to life in the digital age.
What is Morse Code?
Morse Code System is a form of communication that uses a series of dots and dashes to convey letters and numbers.
Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail developed it in the 1830s and 1840s to send messages over long distances using telegraph lines.
Each letter and number in the English alphabet is assigned a remarkable combination of dots and dashes, which can be transmitted as electrical signals or through sound or light signals.
Morse Code was widely used in the early days of telecommunication and is still used today, particularly in maritime and aviation industries.
Logic of Dots and Dashes in Morse Code

The logic behind dots and dashes in Morse Code lies in the representation of letters and numbers using a combination of short and long signals.
Dots are temporary signals that represent the basic unit of time in Morse Code, while dashes are longer signals that have a duration of three dots.
Combining dots and dashes creates a unique pattern for each letter and number in the English alphabet. For example, “A” is represented by a dot followed by a dash, while “B” is represented by a dash followed by three dots.
Using dots and dashes allows for efficient communication using a simple signaling system. Morse Code can represent all the letters, numbers, and punctuation marks using combinations and durations of dots and dashes.
In addition to dots and dashes, Morse Code also includes spaces between letters and words. These spaces help to differentiate between different characters and allow for better readability.
How to Decode Dots and Dashes?
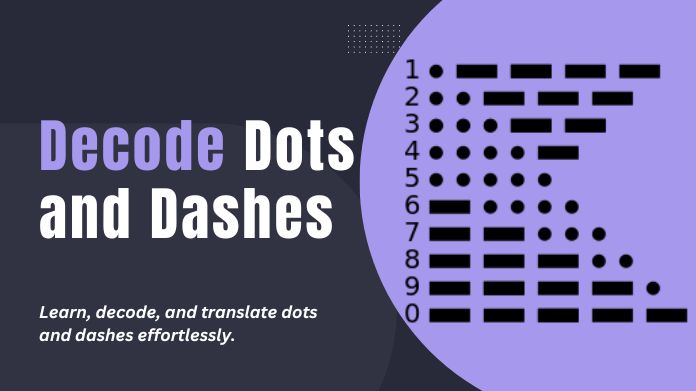
To decode dots and dashes, also known as Morse code, you can follow these steps:
1. Familiarize yourself with the Morse code chart: Morse code consists of combinations of short signals called dots and long signals called dashes. Each letter of the alphabet, as well as numbers and some special characters, has a unique Morse code representation.
2. Start by listening to the dots and dashes: Morse code can be transmitted as sound or visual signals, such as flashing lights. If you are listening to Morse code, pay attention to the duration of the signals. Dots are short sounds or flashes, while dashes are longer.
3. Break the code into individual letters: As you listen to the Morse code, identify the spaces between each letter. Morse code uses short pauses between letters to tell where one letter ends and the next begins.
4. Translate the dots and dashes into letters: Use the Morse code chart to convert them into corresponding letters. For example, a dot followed by a dash represents the letter “A,” while a dash followed by three dots represents “B.”
5. Decode words and sentences: Once you have translated all the letters, group them to form words and sentences. Remember to pay attention to the spaces between words, as Morse code uses longer pauses to indicate where one-word ends and the next one begins.
By following these steps and practising, you can become proficient in decoding Morse code and understand the messages hidden within dots and dashes.
Winding Up!!
In the grand symphony of communication, where every signal carries the echoes of human ingenuity, Morse code stands as a timeless melody.
As we conclude our guide on “Decoding the Dots and Dashes – A Guide to Morse Code Translator,” we find ourselves immersed in this unique communication method’s rich history, versatility, and enduring relevance.
As we bid farewell to this guide, may the dots and dashes linger in your thoughts as more than mere symbols. Let them be a reminder of the intricate language that spans centuries, linking the pioneers of telegraphy to the digital enthusiasts of today.
Whether you embark on a journey to learn Morse code or appreciate its legacy, let the echoes of this guide resonate in your understanding of a communication method that has, and continues to, stand the test of time.
